Cord Blood Banking: Expensive and NOT the Only Option! What If a Decision You DIDN'T Make Could Save Your Child's Life?
Cord Blood Banking: Expensive and NOT the Only Option! What If a Decision You DIDN'T Make Could Save Your Child's Life?
Every expectant mother has dreams for her child. What will my baby look like? Will she be a doctor? An astronaut? A charity worker? A new life is bursting with potential, just waiting on the chance to take the world by storm.
But every expectant mother is also filled with nagging worries. What if the baby isn’t healthy? What if it’s serious? It’s the feeling of helplessness that can be most distressing to parents. There is nothing worse than being unable to help your child when he or she needs you most. If you’re here, then you may have already experienced these concerns. Fortunately, there is something you can do about it that will give you a measure of control over the unknown.
Tooth Stem Cell Banking as an Alternative to Cord Blood Banking
While cord blood banking is a popular option, there are a few disadvantages to it:
- You can only bank cord blood at birth—you only get one chance.
- Cord blood banking is expensive—sometimes prohibitively so.
- Cord blood only yields limited amounts of stem cells, which means donor material from a national or state donor bank may be needed for treating adolescents and adults.
- Cord blood cannot go directly to the site of an injury.
- Cord blood is preprogrammed to turn into blood cells, which significantly limits the clinical applications.
- Cord blood is not capable of regenerating human tissues.

Cord blood yields hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). HSCs have potential for treating diseases that affect the blood because they can turn into any type of blood cell, including white and red blood cells. However, scientists have admitted there are serious limitations with HSCs.
According to the National Institutes of Health, HSCs are not able to replicate, or reproduce themselves. They cannot differentiate—or specialize into other cell types—in a culture dish or test tube. In addition, they cannot be used to treat any disease other than blood diseases and disorders.
And those are just a few reasons why so many modern parents are turning to tooth stem cell banking instead of cord blood banking—or as an addition to cord blood banking. The stem cells extracted from baby teeth or wisdom teeth are called mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Scientists can turn MSCs into nearly any type of cell the body needs, making their potential for clinical application virtually limitless.
Compared to cord blood banking, dental stem cell banking is far more affordable. In addition, MSCs:
- Can be used at any point in life.
- Can be expanded for multiple treatments.
- Offer the capacity for human tissue regeneration.
- Aren’t preprogrammed to only become new blood cells; they can be turned into any cell type for more clinical applications.
- Can go directly to the site of an injury.
In short, dental stem cell banking is the gold standard in regenerative medicine.
With cord blood banking, you only get one chance—upon the birth of your child. But tooth banking offers far more opportunities for banking stem cells later in your child’s life.
When you choose tooth stem cell banking for your child, you’ll have the peace of mind that comes from knowing you’re prepared in case the worst should happen.
The Potential of Stem Cells

Stem cells are the future of medicine, and cord blood banking offers a way to harvest those stem cells and save them for later use. The science of regenerative medicine is downright exciting to think about. What exactly can stem cells be used for? Here’s a look at the clinical treatments and research areas:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Spinal cord injury
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Corneal damage
- Parkinson’s and other neurological diseases
And that’s just the tip of the iceberg. Regenerative medicine is like an insurance policy for your child’s wellbeing. Here’s a closer look at some of the specific clinical applications that dental stem cells might be used for.
- Bone regeneration: In 1966, scientists performed groundbreaking work researching the potential of mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue regeneration. The scientists were able to use the isolated and re-transplanted cells to form new bone in mice. The technique has progressed considerably since 1966. Today, scientists are using stem cells to create a biomaterial “scaffold” that can be transplanted to the bone to encourage bone regeneration. The science is in the pre-clinical stage, and it offers an exciting look at the future of regenerative medicine.
- Heart repair: One of the most devastating legacies of a heart attack is that the damage it inflicts is permanent. When the heart muscle dies after being deprived of oxygenated blood, it can’t be revived… Or can it? Scientists are currently exploring how dental stem cells can be used to regenerate heart muscle tissue in order to restore better cardiovascular function.
- Autoimmune disease treatments: Autoimmune diseases are the problem child of medicine. They include lupus, type 1 diabetes, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It’s confounding to researchers why the body would turn on itself and attack its own healthy tissues. Mesenchymal stem cells are currently being investigated as a potential treatment. They can trigger the production of T regulatory cells, which are responsible for protecting the body from self-attacks caused by immunological malfunctions.
Unlike stem cells collected at birth, dental stem cells can be multiplied. This enables patients to receive multiple treatments as needed for various health conditions.
Opportunities for Dental Stem Cell Banking
Parents are often relieved to discover that, if they didn’t choose cord blood banking, they still have many opportunities to preserve stem cells. One of the many advantages of dental stem cells is that there are multiple chances to bank them at a price point that is far more affordable than cord blood banking.
- Baby teeth: When a baby tooth first starts to wiggle, take your child to the dentist with the Tooth Bank kit.
- Wisdom teeth: Dentists often recommend the preventive extraction of wisdom teeth to avoid complications like tooth impaction. Why not put these teeth to good use, since they’re going to come out anyway?
- Adult teeth: Sometimes, adults who get braces discover that they need to extract a tooth or two to make room during the treatment process. Again, since these teeth need to be extracted anyway, why not bank them for greater peace of mind?
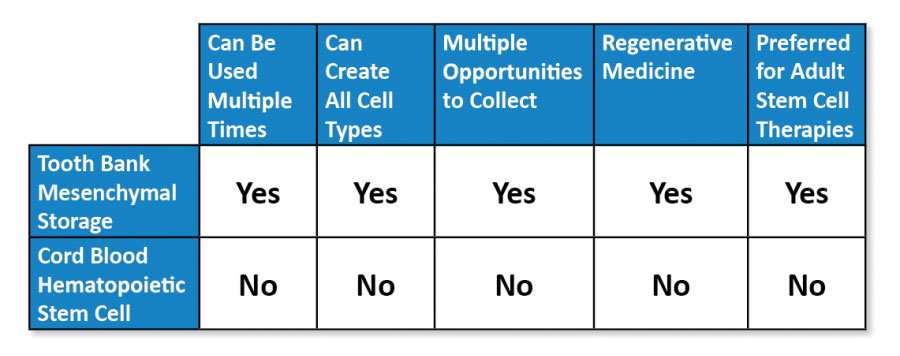
Tooth Banking vs. Cord Blood Banking
Let’s take a closer look at what makes tooth stem cell banking superior to cord blood banking. MSCs are used at a much higher rate than cord blood stem cells. There are also differences in price, collection options, and viability.
Tooth Banking as an Addition to Cord Blood Banking
Some families who have already banked their child’s cord blood may also opt to bank their dental stem cells. As science continues to expand upon the clinical applications for stem cells, having both kinds of stem cells available provides extra insurance for the child’s future. Cord blood stem cells are limited regarding the types of diseases they can treat. For example, cord blood can carry the same diseases that the child may be afflicted with—a problem that makes cord blood stem cells ineffective in the fight against those diseases.
Furthermore, dental stem cells have clinical applications for diseases that affect bones, neurons, muscles, and cartilage, whereas cord blood cells can only be used to treat diseases and cancers of the blood. You could decide to bank your child’s teeth even if you’ve already banked his or her cord blood. By banking both types of cells, parents can give their child an extra safeguard against medical problems.
Peace of Mind for $99

It's tough to put a price on a mother’s peace of mind and a child’s health. But you’ll be relieved to know that tooth stem cell banking is more affordable than cord blood banking. The average cost of cord blood banking in the United States is around $1,300. Tooth Bank recognizes that health is something that should be affordable and accessible to all families.
We’re offering a special discount on tooth stem cell banking—just $99 per year for a total of $595 for the first six years. This price includes everything you’ll need, including shipping the teeth and collecting the stem cells in our state-of-the-art laboratory. Alternatively, you can choose from our convenient and flexible payment plans. And when you enroll now, you’ll get four opportunities to send us your child’s teeth for secure banking.
Here at Tooth Bank, we’re committed to making health accessible. From our family to yours, we hope you’ll join us in the fight to give the next generation the healthiest possible start in life.


